近日,广东医科大学广东省医学分子诊断重点实验室Ishfaq Ahmed(第一作者)、黄功华研究员(通讯作者)等在国际食品顶级期刊《Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety》(IF=12.811)在线发表了题为“Enzymatic crosslinking and food allergenicity : A comprehensive review”的综述论文。

食物过敏已经成为全球关注的主要公共健康问题。在过去的十几年,酶交联技术已经被用于减轻食物过敏的免疫反应性。在开发低过敏性食品时,由于酶交联具有高特异性和选择性优点,其作为一种新非热技术,可以是传统食品加工方法一个很好的替代。通过酪氨酸酶(TYR)、漆酶(LAC)、过氧化物酶 (PO)和谷氨酰胺转胺酶(TG)的酶交联可以修饰食物过敏原结构和生化性质,然后引起变性和抗掩藏抗原表位。LAC、TYR和PO催化酪氨酸侧链氧化来使得蛋白质交联,然而TG能够引起赖氨酸和谷氨酰胺残基异肽键合。酶处理能够产生具有降低的免疫反应性和IgE结合可能性的高分子量交联聚合物。由于更低的免疫刺激潜力有助于Th1/Th2免疫平衡,交联过敏原进一步抑制肥大细胞脱粒。该综述更新了近十年来关于酶交联在减轻食物致敏性上潜在应用的研究,这对于开发低过敏性或无过敏性食品来说很重要。
附:图表
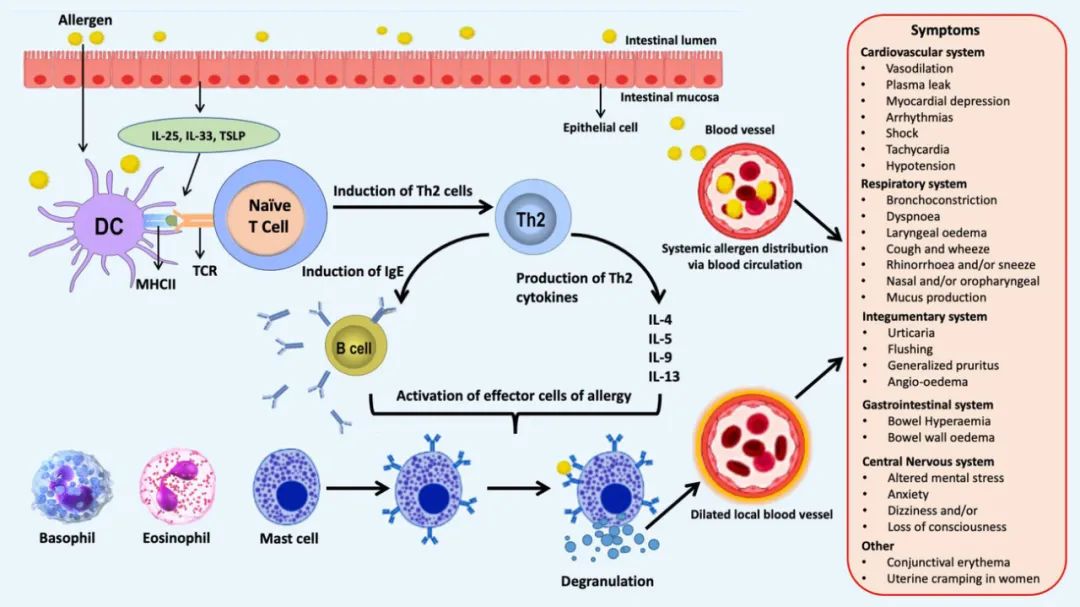
图1 食物过敏原引起的IgE中介反应机制
Food allergens are transported to the intestinal epithelium through paracellular and transcellular mechanisms. The allergens are captured, taken up, and processed by DCs, which subsequently migrate to regional lymph nodes or to sites in the local mucosa upon activation and maturation, where they present allergen-derived peptides in the context of MHC class II molecules to naïve T cells. Naïve T cells then differentiate into Th2 cells, which produce IL-4, IL-6, and IL-13. Likewise, epithelial cells release cytokine alarmins including IL-33, IL-25, and TSLP upon exposure to allergens, that promote the production of Th2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13) by the immune cells of both the innate and adaptive immune systems. Moreover, B cells undergo immunoglobulin class-switching to produce IgE antibodies when the pre-sensitized host is exposed to the food allergens a second time. These IgE antibodies bind to the FcεRI on mast cells and basophils, and result in mast cell degranulation and release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators. These inflammatory mediators promote vasodilation and increased vascular permeability, which contributes to a series of food allergic symptoms.
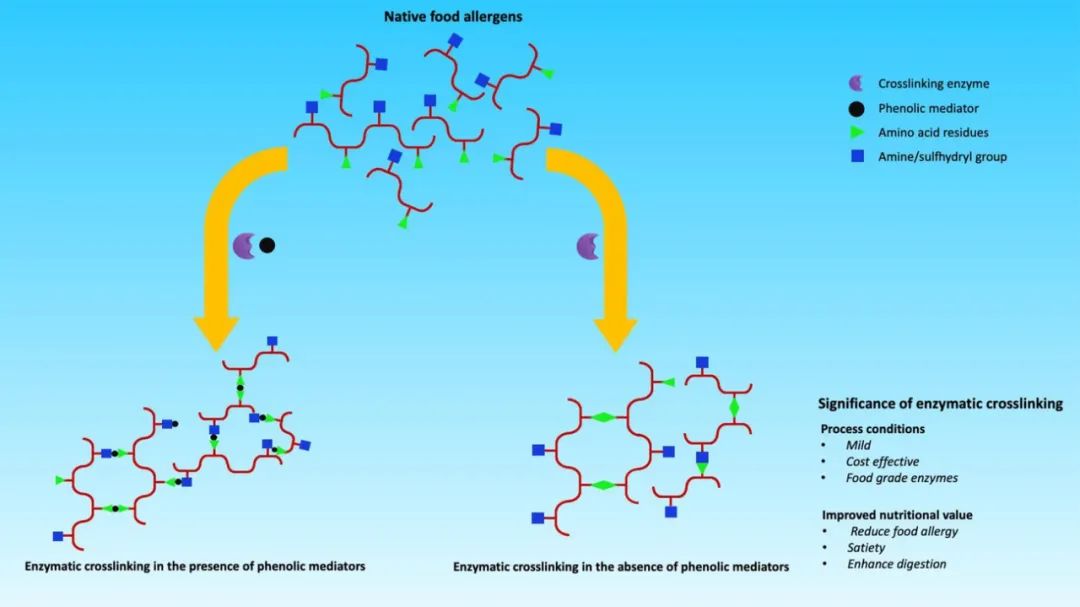
图2 酶催化食物过敏原交联机制
Enzymatic crosslinking produces a high molecular weight polymer through intra- or intermolecular covalent bonds that alter the structural and biochemical properties of food allergens. The reaction mechanisms of each crosslinking enzyme vary based on the amino acid residues with which they react. In the presence of phenolic mediators, oxidative enzymes. The incorporation of phenolic mediators could play a partial role in overcoming the absence of surface-exposed tyrosine residues on the target proteins and also provide the hydroxyl function groups, thereby enhancing the crosslinking efficacy of oxidative enzymes.
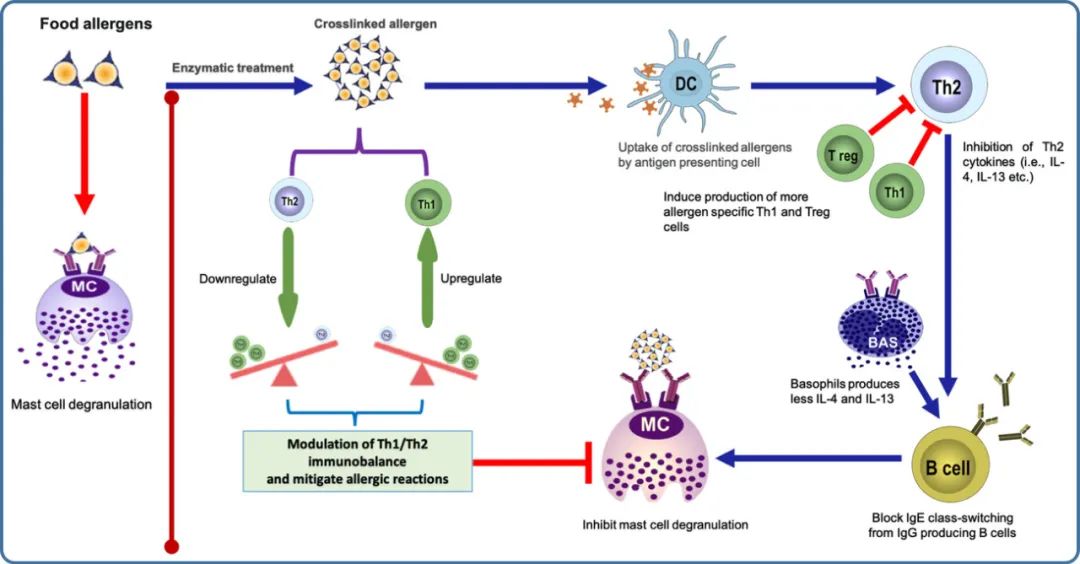
图3 通过酶交联减轻食物致敏性
The immunoreactivity of food allergens decreases upon enzymatic crosslinking due to the formation of polymerized allergen that has reduced binding propensities to IgE antibodies. Allergen uptake of regulatory DCs induces Tregs that cause immune tolerance by effectively suppressing the effector cells of allergy. Tregs cells suppress Th2 cells proliferation and Th2 cytokines by blocking IgE-class switching from allergen-specific B cells. This ultimately results in the alleviation of food allergenicity via reducing basophil activation and mast cells degranulation and restoring Th1/Th2 immunobalance.
表1 交联酶辅助因子、反应机制和反应位点
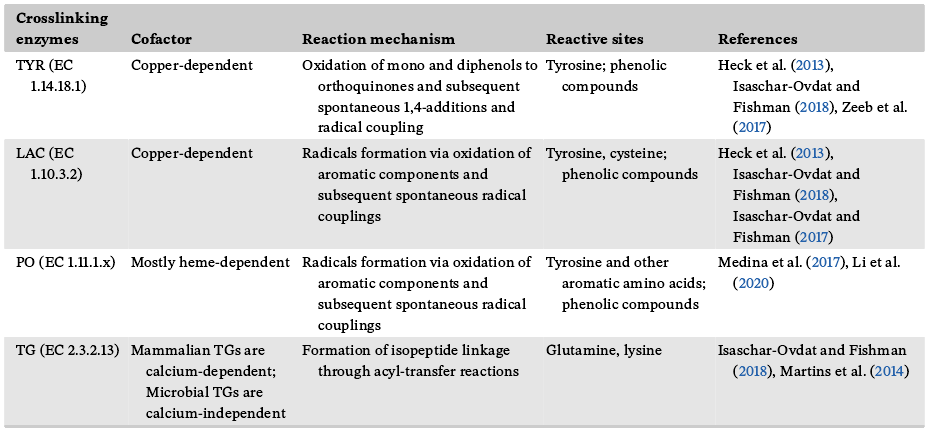
表2 关于通过酶交联减轻贝类过敏原致敏性的最近研究
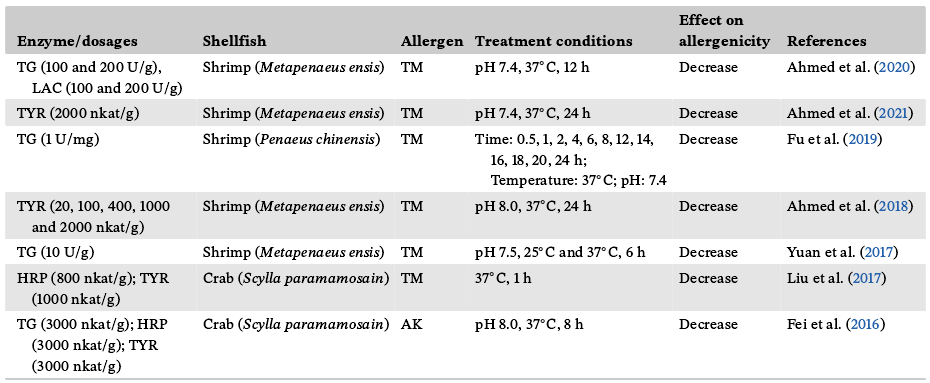
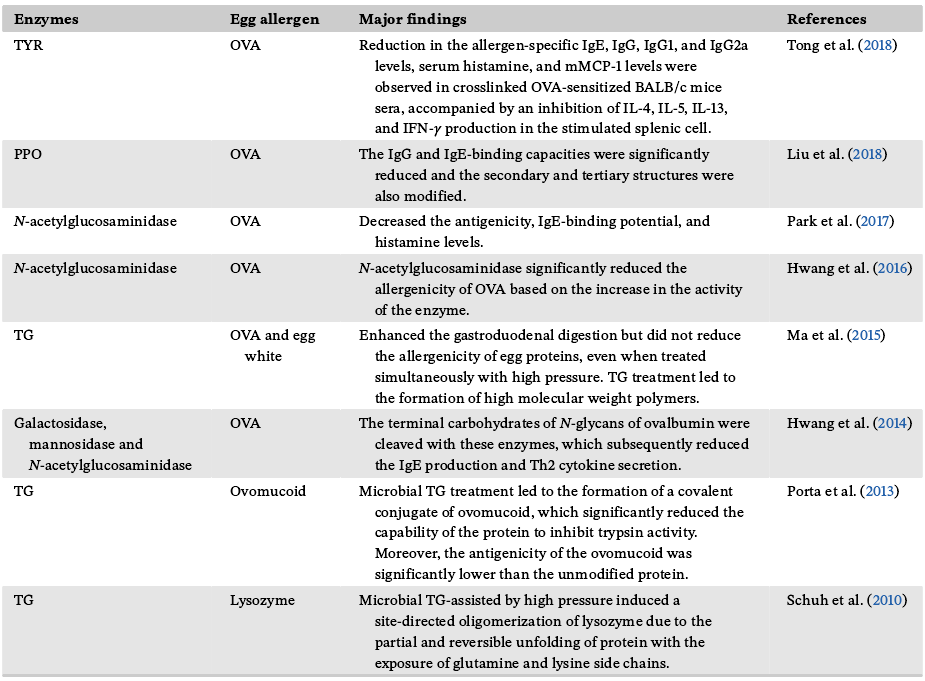
表 3 关于酶处理对鸡蛋过敏原影响的研究
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12855
附:简介
黄功华, 博士,博士生导师,广东医科大学高层次人才,广东省医学分子诊断重点实验室主任,广东省医学分子诊断协同创新发展中心主任。黄功华课题组长期致力于从分子、细胞及动物模型水平研究在生理或病理条件下树突状细胞与免疫微环境中其他细胞复杂的免疫调控网络及其在疾病中的作用机制。取得了一系列原创性科学发现,2011年至今以第一作者或通讯作者在免疫学领域国际知名学术期刊Nature Immunology、Immunity、Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA、Science Signaling 和The Journal of Immunology 等杂志发表论文。2013年9月回国至今,主持科研项目包括国家重点基础研究计划(973计划)、国家重点研发计划、国家自然科学基金面上项目及国家自然科学基金重大研究计划。指导课题组成员获得国家自然科学基金青年项目、中国博士后科学基金面上项目、上海市青年科技英才扬帆计划项目等项目。是美国关节炎研究基金会会士,中国研究型医院学会过敏反应专业委员会青年副主委。